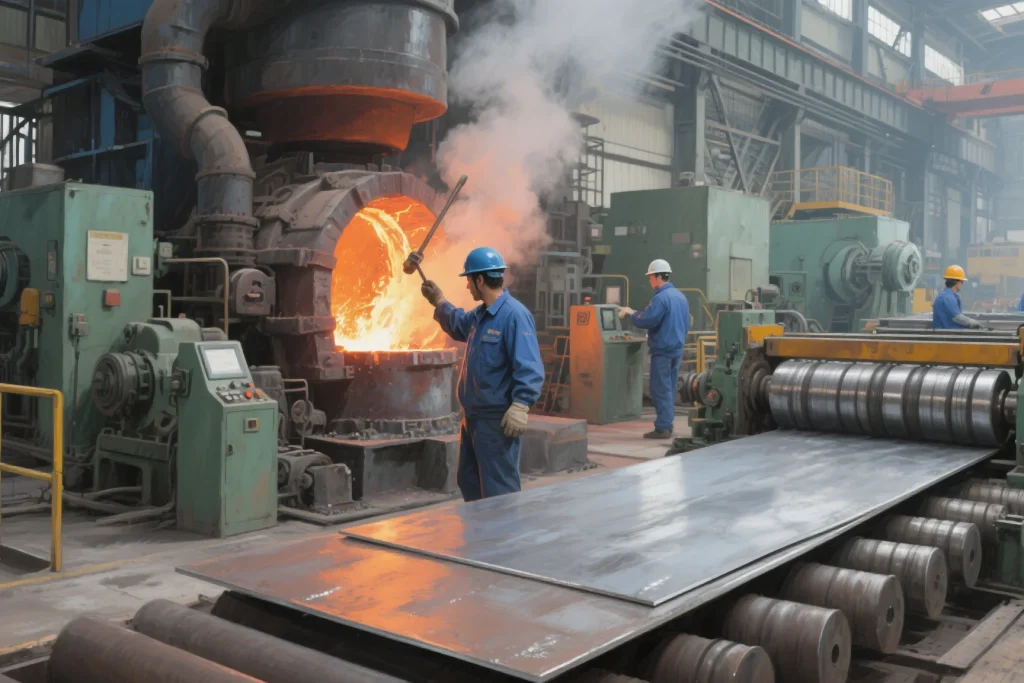
Abrasion resistant сталь doesn’t quit. Engineered to survive punishment in brutal conditions, it’s basically the superhero of metals. Think construction sites chewing through materials or mining equipment grinding all day – that’s where this bad boy shines. The secret sauce? A heavy dose of carbon mixed with special additives that act like body armor. It’s лучшая производительность as nails yet somehow shock-absorbent, meaning fewer breakdowns and more uptime for machines.
Let’s geek out on what makes it work: Carbon forms its backbone, chromium throws punches at wear, and manganese? That’s the flexible friend keeping everything from snapping. This articles will show you the elements in abrasion resistant steel.
1. The Role of Carbon in Истирание Resistant Сталь
Carbon’s Boost to Hardness and Strength
Carbon is a big deal in abrasion resistant steel. It pumps up hardness and strength. More carbon helps the steel stand up to pressure without bending. It’s great for high-impact jobs where the steel needs to hold its shape. During heat treatment, carbon forms hard carbides. These are key to fighting off wear.
Getting Carbon Just Right
More carbon means tougher steel, but it’s a balancing act. Too much can make it brittle. That makes it less able to handle impacts. Manufacturers tweak the carbon carefully. They use smart alloying and heat treatments to nail the right mix of hardness and bendability in abrasion resistant steel like: NM300TP.
2. The Influence of Chromium on Wear Resistance
Chromium’s Toughness Boost
Chromium is a superstar for wear resistance. It makes strong carbides that protect the steel’s surface from friction or abrasive damage. These chromium carbides are tougher than most other parts in steel alloys. They help the material last way longer in harsh conditions.
Chromium’s Corrosion Protection
Chromium doesn’t just stop wear. It also fights rust. Some abrasion resistant steels hold up great in nasty environments. Chromium forms a protective layer on the surface. This keeps moisture or other corrosive stuff from eating away at the steel.
3. The Impact of Manganese in Steel Alloys
Manganese’s Toughness Power
Manganese is another key player. It makes abrasion resistant steel super tough. High-manganese steels, like Mn13, are crazy tough and harden on the surface when stressed. They can take big hits without cracking. This makes them perfect for heavy-duty gear like mining tools or machine parts.
Manganese’s Hardening Trick
Manganese steels have a neat feature: they get harder when stressed. Under heavy hits or pressure, the surface toughens up. Its hardness can jump from HB200 to over HB750. But the core stays flexible. This lets the steel adapt to stress by getting tougher where it’s needed most.
Abrasion resistant steel gets its awesome strength from carefully picked elements. Carbon adds toughness. Chromium fights wear and rust. Manganese boosts flexibility and hardening. By knowing how these work, manufacturers can craft steels perfect for specific jobs. These advances keep abrasion resistant steels ready for the toughest engineering challenges across industries.
4. The Contribution of Nickel to Истирание Resistant Сталь
Nickel’s Flexibility and Toughness
Nickel is a must-have in abrasion resistant steel. It makes the steel bendier and tougher. This steel is known for being hard and strong, standing up to stress without warping. But getting that balance takes careful choices, like adding nickel. Nickel tightens up the steel’s grain, boosting toughness. This is huge for gear facing heavy hits, like mining machines or construction tools.
Nickel also keeps steel tough in cold weather. It performs great in all kinds of climates and work settings. By making steel more flexible, nickel helps it soak up energy without breaking. That’s critical for things like excavator buckets or crusher parts in extreme conditions.
Nickel’s Teamwork with Other Elements
Nickel doesn’t go solo. It works great with chromium and manganese. Chromium makes tough carbides for wear resistance and adds a rust-fighting layer. Nickel helps keep the steel’s structure steady. It spreads carbides and other bits evenly.
Nickel and manganese are a killer combo in high-manganese steels like Mn13. These steels are super tough and harden on the surface. Nickel keeps the steel stable at different temperatures. This mix makes steel that fights wear and toughens up under stress.
5. Silicon as a Strengthening Agent in Steel Alloys
Silicon’s Cleaning and Strengthening
Silicon does a ton for abrasion resistant steel. It cleans the steel during production by sucking out oxygen. This stops weak spots from forming. The result is a stronger, cleaner structure with better performance.
Silicon also toughens the steel by mixing into its core. It boosts hardness without making it too stiff. This makes silicon key for steel plates in heavy machinery or mining gear. The size, shape, and spread of secondary phases affect wear resistance. Silicon fine-tunes these for solid results.
Silicon’s Wear Resistance Boost
Silicon helps steel fight wear by forming tough phases in its structure. Paired with chromium or molybdenum, it makes complex carbides. These are stronger than simpler compounds and form a protective shield on the surface. This cuts down damage from friction or abrasive forces.
Silicon also helps steel hold up in high heat. Parts in metallurgical machines or coking industries love silicon’s strength in hot conditions. High-temperature abrasion resistant steel is great for lightweight, long-lasting parts while saving cash. This makes silicon-boosted steels perfect for spots needing wear resistance and heat toughness.
Nickel and silicon show why alloying elements matter in abrasion resistant steel. They help make materials tailored for tough jobs. These steels stay durable and efficient. Whether you’re in mining or building heavy machines, the right alloy mix can make a big difference in performance and longevity.
В Romispecial®, our abrasion-resistant steel plates—such as NM450, HiAce Corrosion-Resistant Plate, and Mn13—are engineered with optimized alloy compositions to deliver unmatched durability and performance in mining, construction, and industrial processing. Ready to improve wear life and reduce maintenance costs? Связаться с нами today for custom solutions and fast global delivery.
FAQ
Q: Why is carbon important in abrasion-resistant steel?
A: Carbon increases the steel’s hardness and strength, helping it resist deformation under stress. It forms hard carbides during heat treatment, which are key to fighting wear. However, too much carbon can make steel brittle, so it’s carefully balanced for flexibility.
Q: How does chromium improve abrasion resistance?
A: Chromium forms strong carbides that protect the steel’s surface from friction and abrasive damage. It also adds corrosion resistance by creating a protective oxide layer, making the steel suitable for tough, corrosive environments.
Q: What role does manganese play in wear-resistant steel?
A: Manganese boosts toughness and allows the steel to harden under stress. High-manganese steels, like Mn13, can absorb heavy impacts without cracking and increase surface hardness significantly, making them great for high-impact applications.
Q: What is the most widely used abrasion-resistant steel grade?
A: AR400 and AR500 are among the most commonly used abrasion-resistant steels due to their excellent hardness and cost-performance ratio. Other grades like NM450 or Mn13 offer enhanced impact resistance or thermal stability, ideal for mining and metallurgy applications.